Loan Refinance Calculator — Understand Your True Savings
Replace your current loan with a new one to lower your rate, change your term, or reduce your monthly payment. Our free tool shows real savings vs. marketing promises—instantly.
Refinancing means swapping your existing loan for a new one—typically to secure a lower interest rate, extend or shorten the repayment term, or cut your monthly payment. For mortgages, auto loans, student loans, and personal loans, the decision is too important to leave to guesswork.
The Loan Refinance Calculator makes it simple: enter your current balance, APR, and remaining term, then compare against a new loan’s APR, term, and closing costs. You’ll see your new payment, break-even point, lifetime interest, and whether refinancing truly saves money.
Whether you need a mortgage refinance calculator, a refinance car loan calculator, or a general loan refinance calculator, this page gives you transparent math—not just lower-payment teasers.
- New monthly payment vs. current
- Break-even months to recover closing costs
- Total interest: current vs. new loan
- Total savings / loss over the life of the loan
- Exportable CSV & clear charts
Tip: A lower monthly payment doesn’t always mean a cheaper loan. Longer terms can increase total interest. Run the numbers first, then talk to your lender with confidence.
Loan Refinance Calculator
Current Loan
Refinance Loan
New Monthly Payment
Monthly Savings
Break-even (months)
Total Interest (Current)
Total Interest (New)
Total Savings/Loss
How to Use the Loan Refinance Calculator (Step by Step)
Follow these simple steps to compare your current loan against a refinance offer and see payments, savings, break-even, and total interest side by side.
- Balance — the remaining principal you owe today.
- APR (%) — your current interest rate (or APR if disclosed).
- Remaining Term (years) — years left on the current loan.
- New APR (%) — quoted refinance rate (prefer APR if available).
- New Term (years) — the proposed payoff length (e.g., 30 for mortgage, 5–7 for auto).
- Closing Costs ($) — lender, title, or origination fees added to the new loan or paid at closing.
- Click Calculate to see the results instantly.
- Use Reset to clear inputs or try different scenarios.
- Click Export CSV to download results and amortization preview for your records.
Your projected payment under the refinance terms. Lower than your current payment doesn’t always mean cheaper overall if the term is longer.
Difference between your current monthly payment and the new one. Positive values mean you’ll pay less per month.
How long it takes for monthly savings to recover closing costs. If you’ll sell or pay off the loan before this point, the refinance may not be worthwhile.
Lifetime interest for each loan. The calculator highlights which option costs less overall.
Your all-in outcome considering payment schedule and closing costs. A negative value indicates the refinance costs more in total.
 Results panel with payment, savings, break-even analysis, and a balance-over-time chart. Download details with Export CSV.
Results panel with payment, savings, break-even analysis, and a balance-over-time chart. Download details with Export CSV.
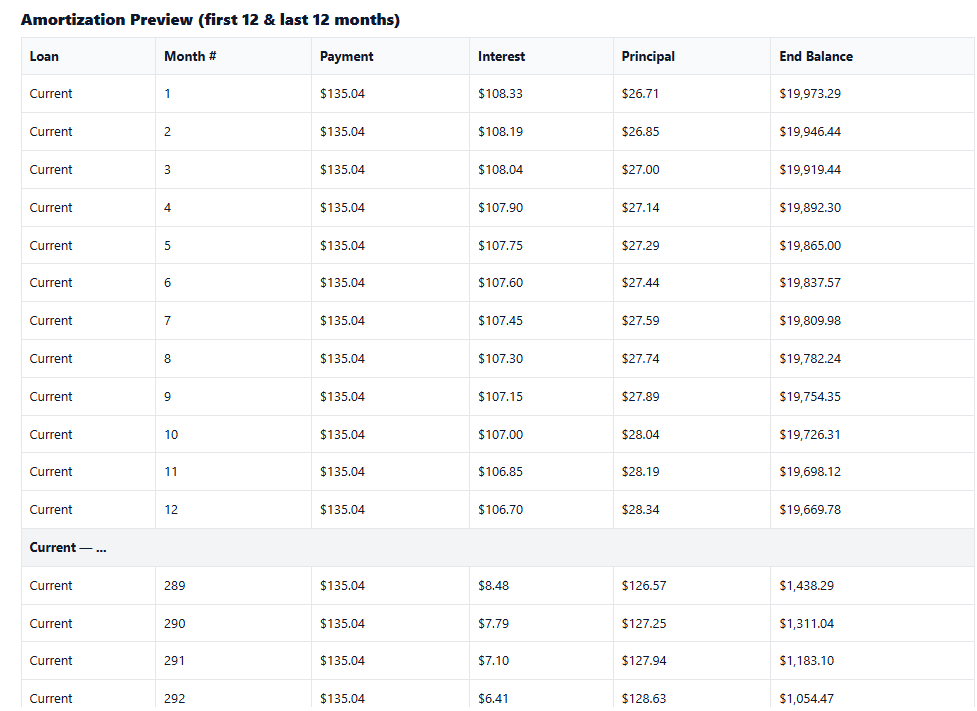
- Compare apples to apples: test the same term on both loans to isolate the effect of the interest rate.
- If the calculator shows No, refinancing will cost more overall, check your closing costs and term length.
- Use the amortization preview to see how interest and principal change over time before you decide.
Keywords: loan refinance calculator, mortgage refinance calculator, refinance car loan calculator.
Calculations & Formulas (Educational Value)
Understanding how loan interest and APR are calculated helps borrowers verify lender quotes and make smarter financial decisions.
Below we break down the formulas behind our Loan Refinance Calculator, so you can follow the math yourself.
📌 Simple Interest Formula
Simple interest is calculated only on the original loan amount (principal). The formula is:
Interest = Principal × Rate × Time
Example: On a $100,000 loan at 6.5% simple interest for 25 years:
Interest = 100,000 × 0.065 × 25 = $162,500 (in addition to the original $100,000).
📌 Compound Interest Formula
Compound interest reflects the fact that interest accrues on both the principal and the accumulated interest. The formula is:
A = P × (1 + r/n)^(n × t)
- A = Final amount
- P = Principal (initial loan)
- r = Annual interest rate
- n = Number of compounding periods per year
- t = Time in years
Example: $100,000 loan, 6.5% APR, compounded monthly, for 25 years:
A = 100,000 × (1 + 0.065/12)^(12 × 25) ≈ $494,229 total owed.
That means $394,229 in interest alone.
📌 APR (Annual Percentage Rate)
APR is more than just the nominal interest rate. It also includes fees, points, and compounding frequency.
To approximate APR, financial analysts use the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) on the loan’s cash flows:
APR = Discount rate where Present Value of all payments = Loan Amount.
This is why our calculator sometimes shows a slightly higher APR than the nominal rate — it factors in fees and timing.
📌 Practical Example
Let’s put it together: $100,000 loan, 6.5% APR, 25 years.
- Monthly Payment ≈ $675.29
- Total Paid Over 25 Years ≈ $202,587
- Total Interest ≈ $102,587
This shows how compounding and loan term dramatically impact your final costs — and why refinancing can save (or lose) thousands depending on the numbers.
Why Refinance Matters
Refinancing is not just about getting a “new loan.” It’s about reshaping your debt in a way that can save you money, reduce your stress, or better align payments with your financial goals.
Whether you are using a refinance mortgage rate calculator, comparing mortgage refinance rates, or testing a refinance rates calculator, understanding the scenarios below is key.
📌 Rate Reduction Refinance
This type of refinance is chosen to secure a lower interest rate. Even a small drop—say from 6.5% to 5.9%—can translate into thousands of dollars in savings over the life of the loan.
The main goal: cut total interest and sometimes lower the monthly payment without extending the term significantly.
📌 Term Extension Refinance
Here, the focus is on lowering the monthly payment by stretching out the repayment term. For example, moving from a 20-year loan to a 30-year loan.
While this makes payments more affordable in the short run, it usually increases total interest paid over time.
📌 The Role of Closing Costs
Every refinance comes with closing costs—such as application fees, appraisal costs, or lender charges.
These upfront expenses can offset the savings of a lower interest rate if you don’t plan to stay in the home or keep the loan long enough to “break even.”
That’s why calculators include break-even months—to show how long it takes for savings to outweigh costs.
📌 APR vs. Interest Rate
A common source of confusion: Interest Rate is the base cost of borrowing, while APR (Annual Percentage Rate) includes interest plus fees and closing costs.
A simplified formula looks like this:
APR ≈ (Total Interest + Fees) ÷ Loan Amount ÷ Years
This is why APR is often higher than the stated rate—it reflects the true cost of borrowing.
Using a refinance calculator that shows both values gives you transparency beyond teaser rates.
✅ Bottom line: Refinancing can either save or cost you money depending on your goals, the rate difference, and the impact of fees. Always evaluate both the monthly benefit and the lifetime cost.
Types of Refinance in the U.S.
In the United States, refinancing is not a one-size-fits-all process. Each loan type—mortgage, auto, student, or personal—comes with its own refinancing strategies, benefits, and risks.
Using the right Loan Refinance Calculator gives borrowers clarity on whether refinancing truly saves money, reduces monthly payments, or simply reshapes debt.
Let’s explore the most common categories in detail.
🏠 Mortgage Refinance
Mortgages are the most common loans refinanced in the U.S. Homeowners often switch from a higher interest mortgage to one with lower rates or different terms.
Two popular paths include:
- 15-Year vs. 30-Year Fixed: A 15-year refinance means higher monthly payments but drastically less interest over time. A 30-year refinance lowers monthly obligations but extends total interest costs.
- Fixed vs. Adjustable (ARM): Some borrowers refinance from a variable-rate mortgage into a fixed loan to lock stability, especially during periods of rising interest rates.
Tools like a mortgage loan refinance calculator or a refinance home loan calculator help estimate monthly savings, break-even points, and lifetime costs.
Many lenders also highlight “refinance housing loan calculator” results to demonstrate potential benefits.
🚗 Auto Loan Refinance
Car owners often refinance auto loans to reduce their monthly payments or secure a lower rate after improving their credit score.
An auto loan refinance calculator or refinance car loan calculator makes it easy to test scenarios:
- Lower APR if credit has improved since the original purchase.
- Shortening the term to pay off the vehicle faster.
- Extending the term to reduce financial pressure but with higher total interest.
Because cars depreciate quickly, refinancing only makes sense if the new terms outweigh remaining interest versus vehicle value.
🎓 Student Loan Refinance
With U.S. student debt surpassing $1.7 trillion, refinancing student loans has become a major strategy for graduates.
Using a student loan refinance calculator allows borrowers to compare current federal or private loans against private refinance options.
Benefits include:
- Lower interest rates for strong credit borrowers.
- Combining multiple loans into one streamlined monthly payment.
- Switching from variable to fixed rates for predictability.
However, refinancing federal loans into private loans can mean losing federal protections (like income-driven repayment or forgiveness options), so calculations are critical before committing.
💳 Personal Loan Refinance
Personal loans are unsecured debts, which means refinancing depends heavily on the borrower’s creditworthiness.
People refinance personal loans to secure a lower rate, extend repayment, or consolidate multiple debts into one.
Since there’s no collateral, lenders assess risk more strictly, making APRs vary widely.
While calculators aren’t as commonly marketed for personal loans, a general loan refinance calculator still helps estimate savings versus fees.
💵 Cash-Out Refinance
A unique type of refinancing, cash-out refinance allows homeowners to replace their existing mortgage with a larger one, withdrawing the difference as cash.
For example: refinancing a $200,000 mortgage into a $240,000 loan provides $40,000 cash at closing.
Borrowers often use this method to fund home renovations, consolidate high-interest debt, or cover large expenses.
The trade-off? Higher loan balance and potentially higher payments. Using a refinance home loan calculator reveals whether the extra debt is sustainable over time.
✅ Bottom line: Whether it’s mortgages, cars, student loans, or personal debt, refinancing can be a powerful financial tool—but only if the math works in your favor.
That’s why pairing lender quotes with a transparent Loan Refinance Calculator is essential before making a decision.
Practical Examples & Scenarios (Case Studies + Screenshots)
These real-world scenarios show how a refinance changes your monthly payment, total interest, and break-even point. Use the tool to plug in your own numbers and confirm the outcome before you commit.
Example 1 — 30-Year Mortgage Refinance (Savings)
Current: $350,000 at 6.50% for 30 years.
Refinance: $350,000 at 5.20% for 30 years, $3,000 closing costs.
- Current monthly ≈ $2,212.24
- New monthly ≈ $1,921.89 → Monthly savings ≈ $290.35
- Break-even ≈ 11 months ( $3,000 ÷ $290.35 )
- Total interest (life of loan): Current ≈ $446,406 vs New ≈ $341,880
- Estimated interest saved ≈ $104,526 (≈ $101,526 after closing costs)
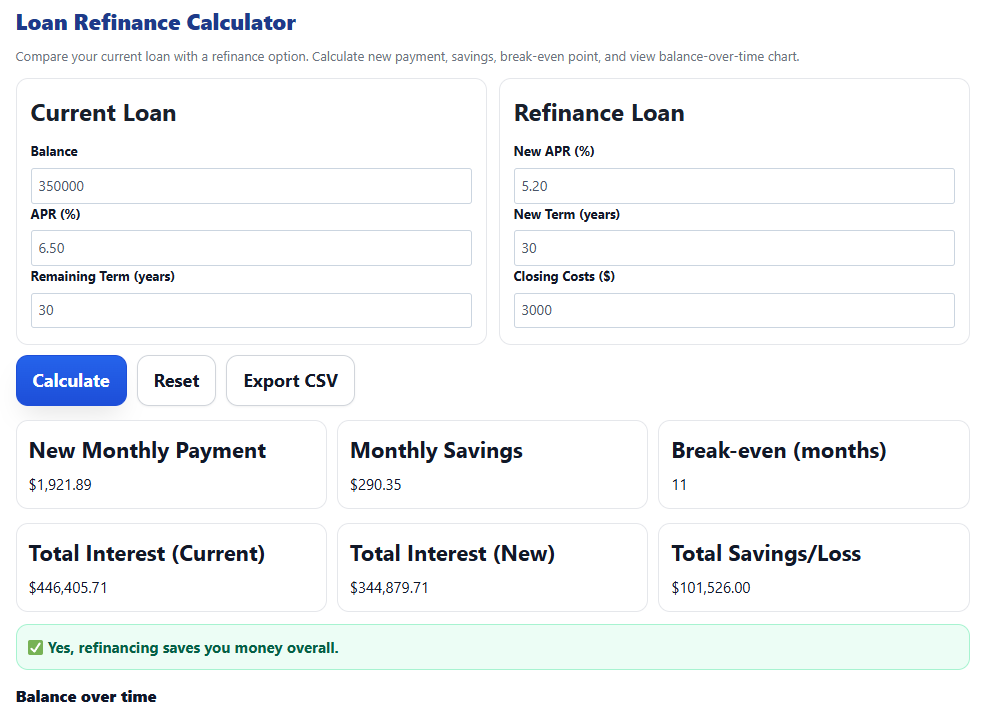 Mortgage refinance example — lower APR, lower monthly payment, clear break-even and lifetime savings.
Mortgage refinance example — lower APR, lower monthly payment, clear break-even and lifetime savings.Example 2 — Auto Loan Refinance (Break-Even)
Scenario: $20,000 auto loan, term 60 months.
Current: 7.50% | Refinance: 5.90% | Title/fees: $150.
- Current monthly ≈ $400.76
- New monthly ≈ $385.73 → Monthly savings ≈ $15.03
- Break-even ≈ 10 months ( $150 ÷ $15.03 )
- Total interest 60 mo: Current ≈ $4,045.54 vs New ≈ $3,143.60
- Estimated interest saved ≈ $901.93
Tip: With cars, small APR drops can still help—but watch fees and how long you plan to keep the vehicle.
Try multiple terms in an auto loan refinance calculator / refinance car calculator to see the sweet spot.
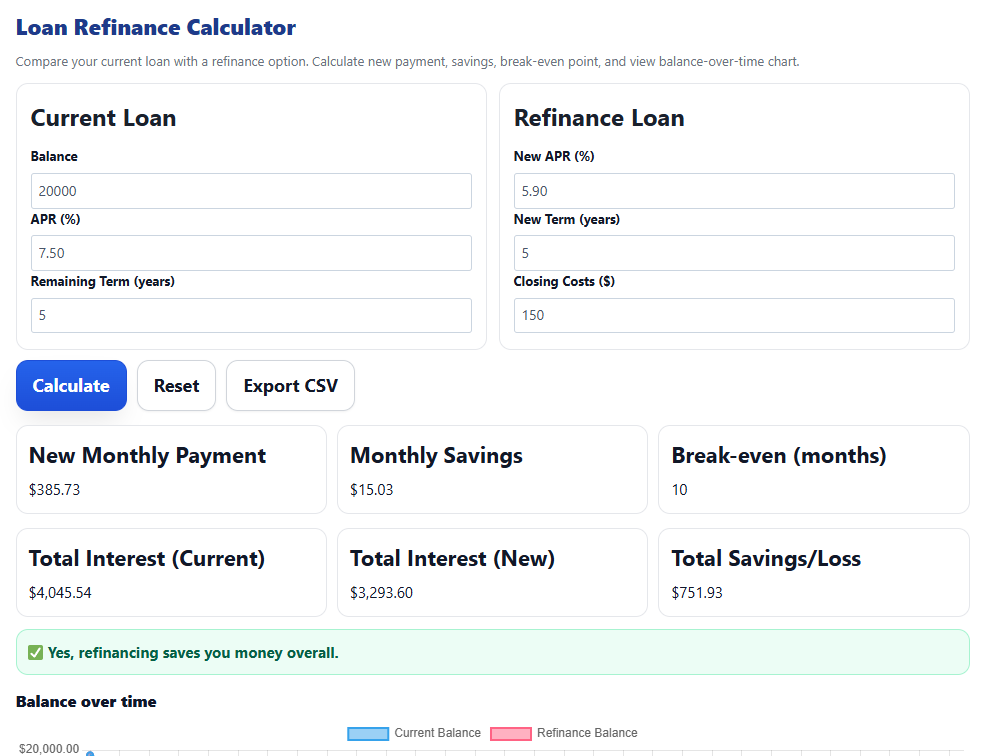 Auto refinance example — small monthly savings add up; break-even driven by fees and holding period.
Auto refinance example — small monthly savings add up; break-even driven by fees and holding period.Example 3 — Student Loan Refinance (Federal vs Private)
Scenario: $45,000 over 10 years.
Current: 6.80% (federal or legacy private) | Refinance: 5.30% (private).
- Current monthly ≈ $517.86
- New monthly ≈ $483.92 → Monthly savings ≈ $33.94
- Total interest 10 yr: Current ≈ $17,143 vs New ≈ $13,070
- Estimated interest saved ≈ $4,073
Caution: Refinancing federal loans into a private loan may remove protections (IDR plans, deferment/forbearance, potential forgiveness).
Always run both scenarios in a student loan refinance calculator and weigh the trade-offs before switching.
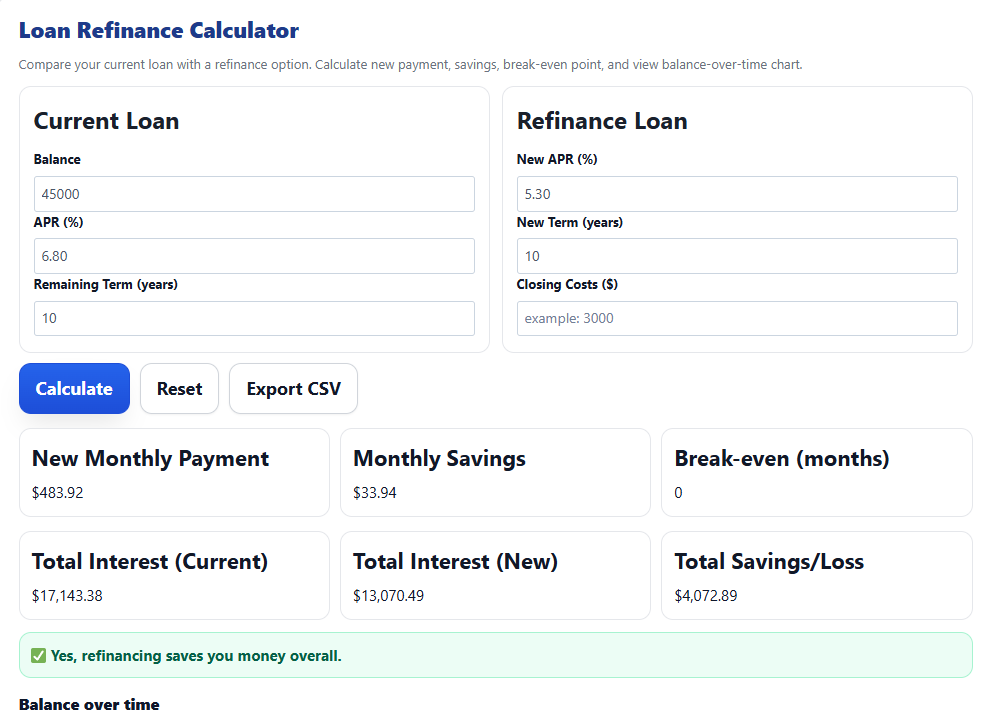 Student refinance example — lower APR helps, but consider loss of federal benefits before choosing private refinancing.
Student refinance example — lower APR helps, but consider loss of federal benefits before choosing private refinancing.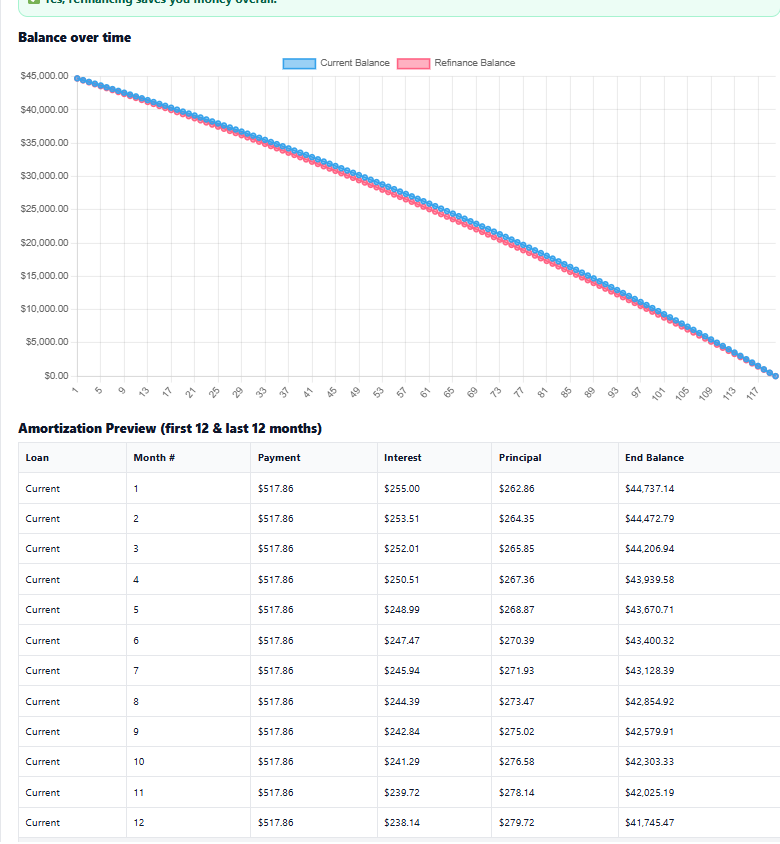
6. Popular Use Cases in the U.S.
Loan refinancing is not just a financial buzzword — it’s a practical tool used every day by millions of Americans. From homeowners to car buyers, and from graduates to individuals consolidating debts,
the Loan Refinance Calculator helps reveal whether refinancing truly makes sense. Here are the most common scenarios:
- Homeowners refinancing mortgages: Many households use a mortgage refinance calculator to lower their interest rate or switch from a 30-year to a 15-year plan.
- Car owners refinancing auto loans: Using an auto loan refinance calculator helps reduce monthly payments or shorten the loan term on vehicles.
- Graduates refinancing student loans: Tools like a student loan refinance calculator compare federal vs. private options to find real long-term savings.
- Debt consolidation: Borrowers with multiple loans may use a loan refinance calculator to combine payments into one streamlined schedule — often at a lower blended rate.
💡 Refinancing isn’t always right — use the calculator to know for sure.
7. Pros & Cons of Refinancing
Refinancing a loan can be a smart financial move, but it’s not always the right choice for everyone.
The Loan Refinance Calculator helps you weigh the benefits against the potential drawbacks before making a decision.
✅ Pros
- Lower interest rates: Secure a better deal when market rates drop.
- Lower monthly payments: Free up monthly cash flow for other expenses.
- Faster payoff: Shorten your loan term and save on total interest.
❌ Cons
- High closing costs: Fees and charges can offset your savings.
- Longer debt period: Extending your loan may increase total interest paid.
- Risk of higher cost overall: Without careful planning, refinancing can cost more in the long run.
💡 Tip: Always compare your break-even point with your financial goals before refinancing.
FAQs — Loan Refinance Calculator & U.S. Refinancing Basics
Quick answers to the most searched questions about mortgage, auto, student-loan and personal-loan refinancing in the U.S.
Use these with our free loan refinance calculator to run the numbers before you apply.
1) What is a refinance loan?
You’ll pay closing costs on many mortgages (and sometimes on other loans). Use a calculator to see if the savings exceed the costs within your time horizon.
2) When should I refinance my mortgage?
break-even point, or you want to shorten the term. Run the scenario in the calculator and compare the break-even months to how long you’ll keep the home.
3) How do closing costs affect refinancing?
Divide total costs by monthly savings to estimate months to break even. If you’ll sell or refi again before then, it may not be worth it.
4) Is refinancing a car loan worth it?
Use the refinance car loan calculator setting to compare your current APR/term vs. a new APR/term plus any title/transfer fees.
5) What’s the difference between refinance APR and interest rate?
When comparing lenders, look at monthly payment, total interest, and APR—not rate alone.
6) Is a 20-year refinance better than a 30-year?
If cash-flow is tight, 30-year may feel safer; if you can afford it, 20-year builds equity faster. Model both in the calculator.
7) What are 20 year refinance rates right now?
calculator to see payments and lifetime interest. Search term: 20 year refinance rates.
8) What are current 30-year mortgage rates?
9) How do I calculate a mortgage payment?
P · r / (1 − (1+r)−n), where P=principal, r=periodic rate, n=# of periods.A mortgage calculator or our refi tool handles compounding and fees automatically—and exports CSV if needed.
10) simple mortgage calculator vs refinance calculator—what’s the difference?
includes closing costs, and computes break-even and total savings/loss.
11) “Mortgage news daily” says rates moved—should I refinance?
12) Mortgage refinance rates September 2025—what should I expect?
13) Mortgage rate predictions—wait or refinance now?
14) Mr. Cooper, Rocket Mortgage, Chase, U.S. Bank calculators—should I use them?
15) What is a mortgage refinance break-even calculator?
16) What does Redfin have to do with refinancing?
17) What is a cash-out refinance?
18) Does refinancing hurt my credit score?
19) Can I refinance federal student loans?
20) Where does “loan refinance calculator” fit in my decision?
If the calculator shows negative net savings (or a very long break-even), refinancing may not be right now.
Tip: Rates and lender policies change frequently. Re-run your scenarios whenever you get a new quote or your credit profile changes.
Conclusion — Should You Refinance?
Refinancing can be a powerful financial tool to lower your rate, reduce your monthly payments, or shorten your payoff timeline.
But it’s not always the best move. High closing costs, longer debt terms, or a very late break-even point can make refinancing less attractive.
That’s why our free Loan Refinance Calculator helps you make an informed decision—based on transparent numbers, not marketing promises.
Explore More Free Calculators
- Loan Payoff Calculator — See how fast you can become debt-free.
- Loan Interest Calculator — Compare interest, APR, and total cost.
- Loan Comparison Calculator — Stack different loan offers side by side.
Trusted External Resources
- CFPB Guides — U.S. Consumer Financial Protection Bureau resources on refinancing & borrower rights.
- Federal Student Aid — Learn about student loan refinancing, repayment, and forgiveness options.
Take control of your loan — compare, calculate, and refinance smart today.
